Sunday, October 28, 2012
Saturday, September 29, 2012
Saturday, September 22, 2012
Create the water mark Textbox;
http://codingcluster.blogspot.in/2011/08/watermark-textbox-using-javascript.html
http://codingcluster.blogspot.in/2011/08/watermark-textbox-using-javascript.html
Sunday, September 16, 2012
How to use the MVC Application?
Use MVC Applciation?
“M” “V” “C” stands for “MODEL” “VIEW” “CONTROLLER”. ASP.NET MVC is an architecture to develop ASP.NET web applications in a different manner than the traditional ASP.NET web development. Web applications developed with ASP.NET MVC are even more SEO (Search Engine) friendly.
Developing ASP.NET MVC application requires Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 or higher.
Inside the ROOT directory of the application, there must be 3 directories each for model, view and Controller.
Apart from 3 directories, there must have a Global.asax file in root folder, and a web.config like a traditional ASP.NET application.
A step by step process is explained below [Refer to the figure as given below]:

So for [xyz.com]/home/index/:
There can be more than one action method, but MVC will only invoke the action method which has been parsed from the URL, its
So something like:
Invoking action method can return plain text string OR rendered HTML by using view.
In our case, controller was home and action was
This is it, the whole process ends here. So this is how MVC architecture works..
All the Best....
Introduction
This article is intended to provide basic concepts and fundamentals of ASP.NET MVC (Model View Controller) architecture workflow for beginners.“M” “V” “C” stands for “MODEL” “VIEW” “CONTROLLER”. ASP.NET MVC is an architecture to develop ASP.NET web applications in a different manner than the traditional ASP.NET web development. Web applications developed with ASP.NET MVC are even more SEO (Search Engine) friendly.
Developing ASP.NET MVC application requires Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 or higher.
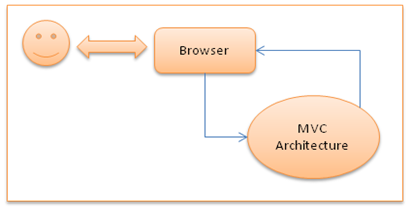
MVC Interaction with Browser
Like a normal web server interaction, MVC application also accepts requests and responds to the web browser in the same way.
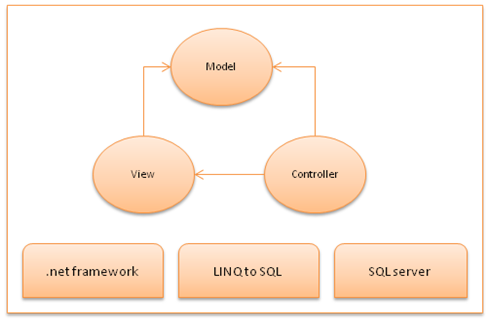
Inside MVC Architecture
The entire ASP.NET MVC architecture is based on Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 and in addition uses LINQ to SQL Server.What is a Model?
- MVC model is basically a C# or VB.NET class
- A model is accessible by both controller and view
- A model can be used to pass data from Controller to view
- A view can use model to display data in page.
What is a View?
- View is an ASPX page without having a code behind file
- All page specific HTML generation and formatting can be done inside view
- One can use Inline code (server tags ) to develop dynamic pages
- A request to view (ASPX page) can be made only from a controller’s action method
- Controller is basically a C# or VB.NET class which inherits system.mvc.controller
- Controller is a heart of the entire MVC architecture
- Inside Controller’s class action methods can be implemented which are responsible for responding to browser OR calling views.
- Controller can access and use model class to pass data to views
- Controller uses ViewData to pass any data to view

MVC File Structure & File Naming Standards
MVC uses a standard directory structure and file naming standards which are a very important part of MVC application development.Inside the ROOT directory of the application, there must be 3 directories each for model, view and Controller.
Apart from 3 directories, there must have a Global.asax file in root folder, and a web.config like a traditional ASP.NET application.
- Root [directory]
- Controller [directory]
- Controller CS files
- Models [directory]
- Model CS files
- Views [directory]
- View aspx/ascx files
- Global.asax
- Web.config
- Controller [directory]
ASP.NET MVC Execution Life Cycle
Here is how MVC architecture executes the requests to browser and objects interactions with each other.A step by step process is explained below [Refer to the figure as given below]:

Browser Request (Step 1)
Browser request happens with a specific URL. Let’s assume that the user enters URL like: [xyz.com]/home/index/Job of Global.asax – MVC routing (Step 2)
The specified URL will first get parsed viaapplication_start() method inside Global.asax file. From the requested URL, it will parse the Controller, Action and ID.So for [xyz.com]/home/index/:
- Controller = home
- Action = index()
- ID = empty — we have not specified ID in [xyz.com]/home/index/, so it will consider as empty string
Controller and Action methods (Step 3)
MVC now finds the home controller class in controller directory. A controller class contains different action methods,There can be more than one action method, but MVC will only invoke the action method which has been parsed from the URL, its
index() in our case.So something like:
homeController.index() will happen inside MVC controller class.Invoking action method can return plain text string OR rendered HTML by using view.
Call to View (Step 4)
Invoking view will returnview(). A call to view will access the particular ASPX page inside the view directory and generate the rendered HTML from the ASPX and will respond back to the browser.In our case, controller was home and action was
index(). So calling view() will return a rendered HTML from the ASPX page located at /views/home/index.aspx.This is it, the whole process ends here. So this is how MVC architecture works..
All the Best....
Saturday, September 15, 2012
Dot Net Interview!!!!
.Net Interview Prepration????
Give an example of using querystrings to send data from one page to another?
Query strings are a very simple and popular technique to pass data from one Web page to the next. You send data as part of the URL. In the below example FName and LName are sent as part of the URL. In the page load of QueryStrings2.aspx we use Request.QueryString to read the values. As we are sending more than one query string we use the & symbol to seperate query strings.//Code to send query strings FName and LName as part of the URLQueryStrings2.aspx?FName=David&LName=Boon protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Code to read Query String values
string FirstName = Request.QueryString["FName"];
string LastName = Request.QueryString["LName"];
Response.Write("Data from QueryStrings1.aspx : " + FirstName + ", " + LastName);
}
Give an example to send Query Strings from code?
You can send query strings from server side code using the Response.Redirect() method as shown below.Response.Redirect("QueryStrings2.aspx?FName=David&LName=Boon");
What are the advantages of using Query Strings?
1. Query strings are easy to implement.
2. Browser support for passing values in a query string is nearly universal.
3. Query strings are contained in the HTTP request for a specific URL and do not require server resources.What are the disadvantages of using querystrings to send data from one page to another?
1. Query strings are insecure because the information in the query string is directly visible to the user on the address line in the browser.
2. Many browsers impose a 255 URL character limit which can limit their flexibility.
Give an example of using querystrings to send data from one page to another?
Query strings are a very simple and popular technique to pass data from one Web page to the next. You send data as part of the URL. In the below example FName and LName are sent as part of the URL. In the page load of QueryStrings2.aspx we use Request.QueryString to read the values. As we are sending more than one query string we use the & symbol to seperate query strings.//Code to send query strings FName and LName as part of the URLQueryStrings2.aspx?FName=David&LName=Boon protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Code to read Query String values
string FirstName = Request.QueryString["FName"];
string LastName = Request.QueryString["LName"];
Response.Write("Data from QueryStrings1.aspx : " + FirstName + ", " + LastName);
}
Give an example to send Query Strings from code?
You can send query strings from server side code using the Response.Redirect() method as shown below.Response.Redirect("QueryStrings2.aspx?FName=David&LName=Boon");
What are the advantages of using Query Strings?
1. Query strings are easy to implement.
2. Browser support for passing values in a query string is nearly universal.
3. Query strings are contained in the HTTP request for a specific URL and do not require server resources.What are the disadvantages of using querystrings to send data from one page to another?
1. Query strings are insecure because the information in the query string is directly visible to the user on the address line in the browser.
2. Many browsers impose a 255 URL character limit which can limit their flexibility.
Friday, September 14, 2012
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)